
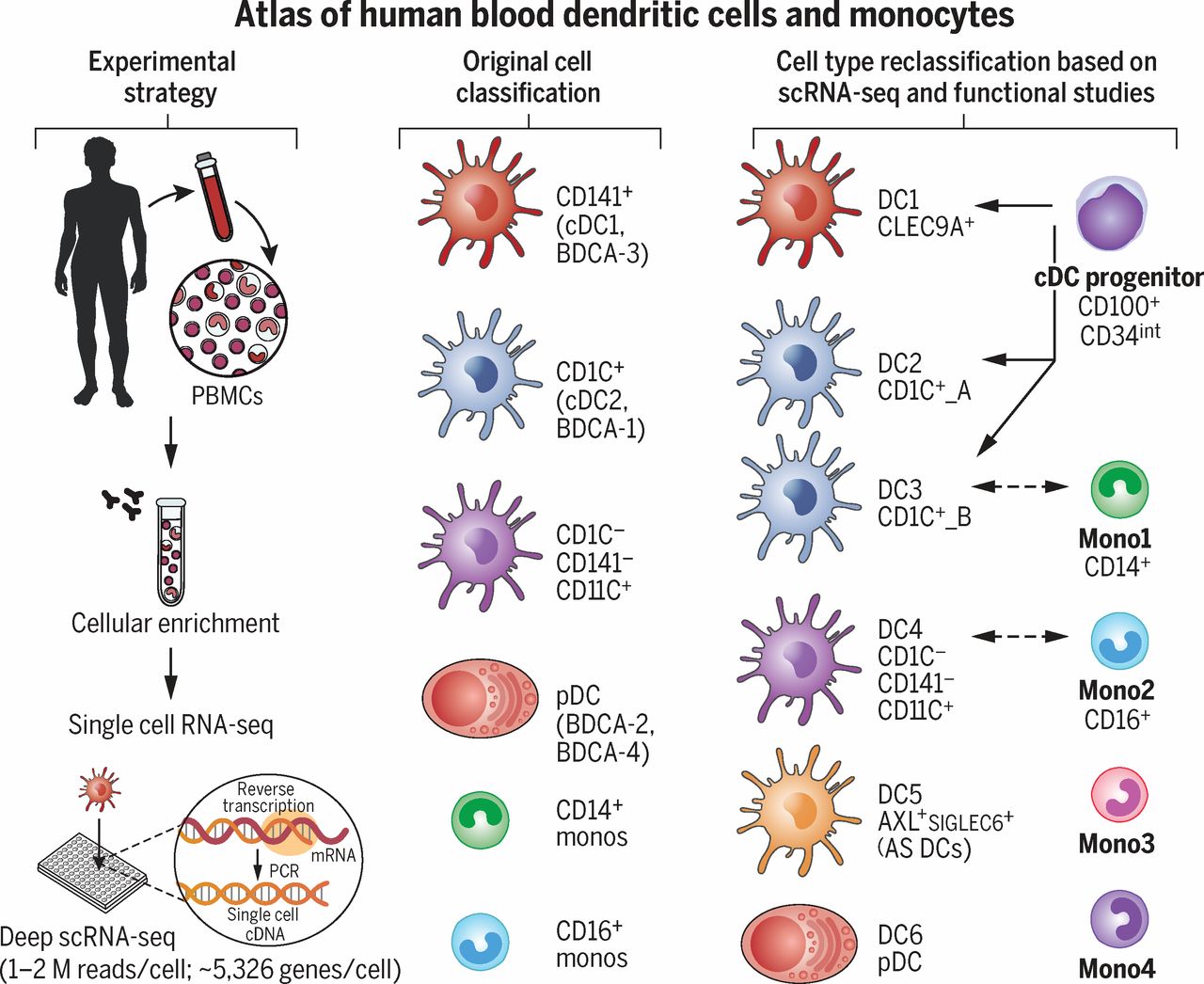
muciniphila resulted from polyphenol compounds contained in tempeh. muciniphila) levels, which can improve type 2 diabetes and obesity. Some studies have shown that the concentration of salivary secretory IgA and natural killer cells decreased after prolonged HIE, and that paraprobiotics can help activate plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), a pivotal member of the immune system.Ī study also showed that daily consumption of 100g of steamed tempeh for 16 days boosted IgA production and Akkermansia muciniphila ( A. “The close relationship between immunity and fatigue may be the cause of increased susceptibility to viral infections, especially since high-intensity exercise (HIE) can increase the risk of upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs),” said the authors.įor athletes, increased fatigue and reduced immunity are serious problems. It is usually consumed after first being cooked, with the heat causing the probiotics to become inactive (paraprobiotics).Īlthough paraprobiotics are inactivated bacteria, a number of studies have established that they play an important role in the gastrointestinal microbiota ecosystem and immune system, reducing oxidative stress and fatigue, and increasing muscle mass in different pathways.įor instance, the paraprobiotics in tempeh can induce gene expression in the Immunoglobulin A (IgA) gene, an antibody that defences against antigens in the mucosal membrane. Tempeh is made via fermentation using beneficial microorganisms such as enzyme-secreting mould and lactic acid bacteria. Notably, a recent systematic review and meta-analysis showed that L-arginine supplementation can enhance anaerobic ( breakdown of glucose without using oxygen) performance in athletes,” the authors wrote. “ One of the abundant amino acids in tempeh is L-arginine, which is beneficial for reducing fat formation in the body.
To evaluate the potential effect of tempeh on sports performance, researchers from Indonesia and Italy conducted a review of published literature and recent findings. It contains amino acids including methionine, threonine, valine, leucine, phenylalanine and isoleucine that have been found to help muscle growth. Plant-based protein can be obtained from tempeh, a fermented soybean product originated from Indonesia. Muscle synthesis and recovery are crucial to improve sports performance, and protein is one of the most consumed nutrients by athletes to stimulate muscle growth and repair.Īlthough sports nutrition foods are still dominated by animal-based ingredients, such as meat, eggs and milk, there has been a growing demand for plant-based alternatives due to environmental concerns and health problems such as deficiency in digesting lactose. Emulsifiers, stabilisers, hydrocolloids.Chocolate and confectionery ingredients.Carbohydrates and fibres (sugar, starches).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
